Key Takeaways
- G-code vs M-code: G-code and M-code are two sets of commands in the same CNC language. G-code controls the geometry and movement of the machine, while M-code controls the miscellaneous functions and actions of the machine.
- G-code examples: G-code commands start with the letter G, followed by a number from 0 to 99. For example, G0 means rapid positioning, G1 means linear interpolation, and G2 means circular interpolation clockwise.
- M-code examples: M-code commands start with the letter M, followed by a number from 0 to 99. For example, M3 means spindle on clockwise, M5 means spindle off, and M8 means coolant on.
- CNC software: CNC software can help design and generate the CNC code for machining. CAD-CAM software can create both G-code and M-code based on the CAD design and the desired settings. CNC software can also be used to inspect and modify the code if needed.
G and M codes are two sets of commands integral to CNC, as well as other manufacturing methods like 3D printing.
Most people may only have heard of G-code, but M-codes are equally as important. Both G codes and M codes affect the CNC machining process, but control different aspects.
What Are G Code and M Code?
G-code refers to “geometry” code which instructs movement across the CNC machine’s axes. M-code means “miscellaneous” code which controls various other functions, like coolant, the direction the spindle spins in, or the opening of the door.
In CNC programming, we use a computer file that instructs the CNC what to do. This is usually a .NC file type, containing code that the CNC machine will understand.
The CNC language in an NC file consists of “words” that start with letters, and contains G and M-codes.
For example, below are two lines of code in a CNC code file. The first contains a G-code, the second contains M-code.
- N80 G0 Z5
- N81 M5
For the first example using G-code in the bullet point above, this means that on line 80 of the code (N80) move at high speed (G0) on the Z axis to coordinate 5 (Z5).
For the second example, it means on line 81 of the code (N81), turn off the spindle (M5).
Each line of the CNC code represents a proverbial “sentence.” Every line (each sentence) has a command. The two words G0 and M5 are commanding words, telling the machine what to do.
So, to program a CNC, we use G words and M words to command the machine to do various tasks – or as some call them, G-codes and M-codes.
But, it’s important to remember that G-codes and M-codes are not two different codes in two different languages. They are different commands, within the same CNC language.
It’s just that because G-code is the most common command in CNC programming, that G-code has become a popular and common way to refer to the entire CNC code.
The Other Letters In CNC Code (Beyond G and M)
These four letters represent the important CNC commands:
- G: Geometry commands
- M: Miscellaneous commands
- F: set feed rate (command)
- S: set spindle speed (command)
Other letters are not commands, but specify something. For example, below are some other letters in CNC code:
- X: corresponds to the x-axis
- Y: corresponds to the y-axis
- Z: corresponds to the z-axis
- A: corresponds to the A axis
We also have a whole article on the letters I, J, K, and R in CNC programming.
Now, let’s discuss in more detail the most important commands in CNC code: G codes and M codes.
G-code
The “G” in “G-code” refers to geometry, and these instructions control the co-ordinates where the machine should move, to accurately form the part. These instructions tell the machine where to move to fabricate the part.
Instructions written in G-code include where and how to move, where to start, where to stop, and how quickly to move the spindle.
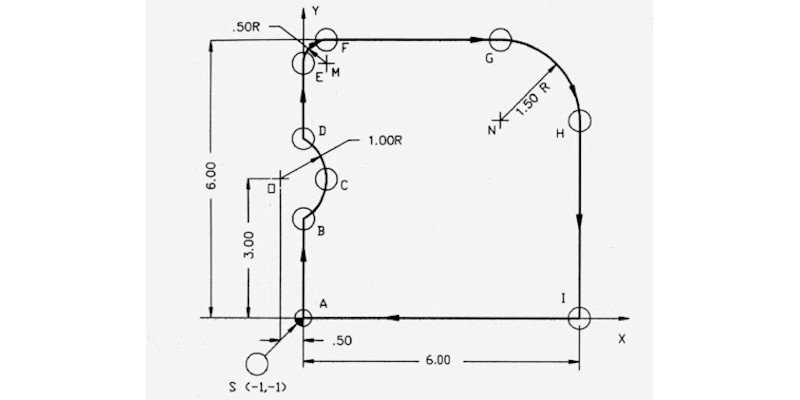
G codes comprise a number of other letters, and while the G part of the code tells the machine when to do (command part of the code), other letters like X, Y and Z tell where to move within each of these three cartesian dimensions.
There are about 100 G code commands, from G0 to G99. However, not all CNC machines are compatible with all of these G codes.
These are some of the most important G-codes that I’ve picked as examples:
| G Code | Command Meaning |
|---|---|
| G0 | Move at rapid speed |
| G1 | Move at feed rate speed |
| G2 | Move on circle arc clockwise |
| G3 | Move on circle arc counterclockwise |
| G4 | Dwell – pause |
| G40 | Cancel cutter compensation |
| G41 | Compensate cutter diameter to the left of path |
| G42 | Compensate cutter diameter to the right of path |
| G43 | Compensate cutter length |
M-code
The “M” references miscellaneous or machine code, and covers all the major instructions not covered by the G-code. Rather than geometric alphanumeric movements, M-codes instruct the CNC machine to start and stop certain actions or programs outside the G-code’s domain.
These instructions include when to use coolant, when to open the machine doors, when to change the direction the spindle spins in, or to change tools.
Here are some important M codes:
| M Code | Command Meaning |
|---|---|
| M3 | Turn on spindle clockwise |
| M4 | Turn on spindle counter clockwise |
| M5 | Turn off spindle |
| M7 | Turn on coolant in mist mode |
| M8 | Turn on coolant in flood mode |
| M9 | Turn off colant |
| M98 | Call and execute subroutine program |
| M99 | Return from subroutine to main program |
CAD-CAM software and generating G-code and M-code
Rather than programming CNC software code by hand, CAD-CAM software can both design and prepare your eventual part for production and produce these CNC files.
CAD-CAM software takes your CAD design, and your desired settings, and uses this to generate your G-codes for machining.
Some experts may want to inspect and modify codes if they believe this could lead to a better quality part, but if you’re a beginner, you may prefer to just go with the code that the software generates.
For more information, we also have a guide to the best CNC software and become familiar with the technical jargon, do read our comprehensive guide to CNC terminology.
- We also have a ranking of the best CNC machines.
- We also have a ranking of the best DIY CNC routers.
- We also discussed the differences between an NC vs CNC machine