CNC machining is a powerful technology that automates the carving, drilling, and shaping of materials. It only requires programming specific parameters into a machine and letting it do all the heavy lifting for us.
These machines can cut materials like wood and metal with detail that was once only achievable by expertly skilled craftsmen.
CNC machines have been a major boom for a lot of industries, and here we’re going to look at how the CNC industry itself has been impacted by this widespread – and growing – use. Check out these interesting CNC industry facts to learn more.
Key Facts about the CNC Industry
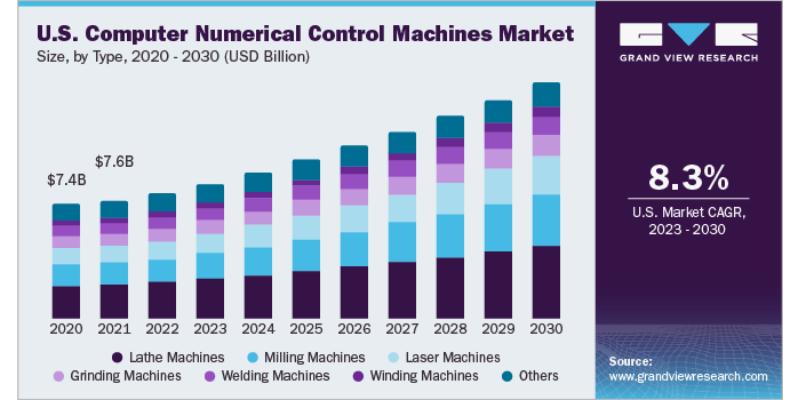
- The CNC industry is expected to reach $15 billion by 2026.
- The demand for automation, precision, and efficiency in several sectors has spurred the continuous growth of the CNC industry.
- Lincoln Electric, Fanuc, Haas Automation, and Siemens are leaders in the CNC industry.
- The trend of Manufacturing as a service (MaaS) is expected to continue in the CNC industry because of the flexibility and cost-effectiveness it provides businesses. [8]
- The Asia Pacific Region held over 35.9% of the global market share in 2022. [9]
- Haas was one of the top CNC market contributors in 2021, holding an estimated worth of $250 million in 2023. [12]
Facts About the History & Evolution of the CNC Industry
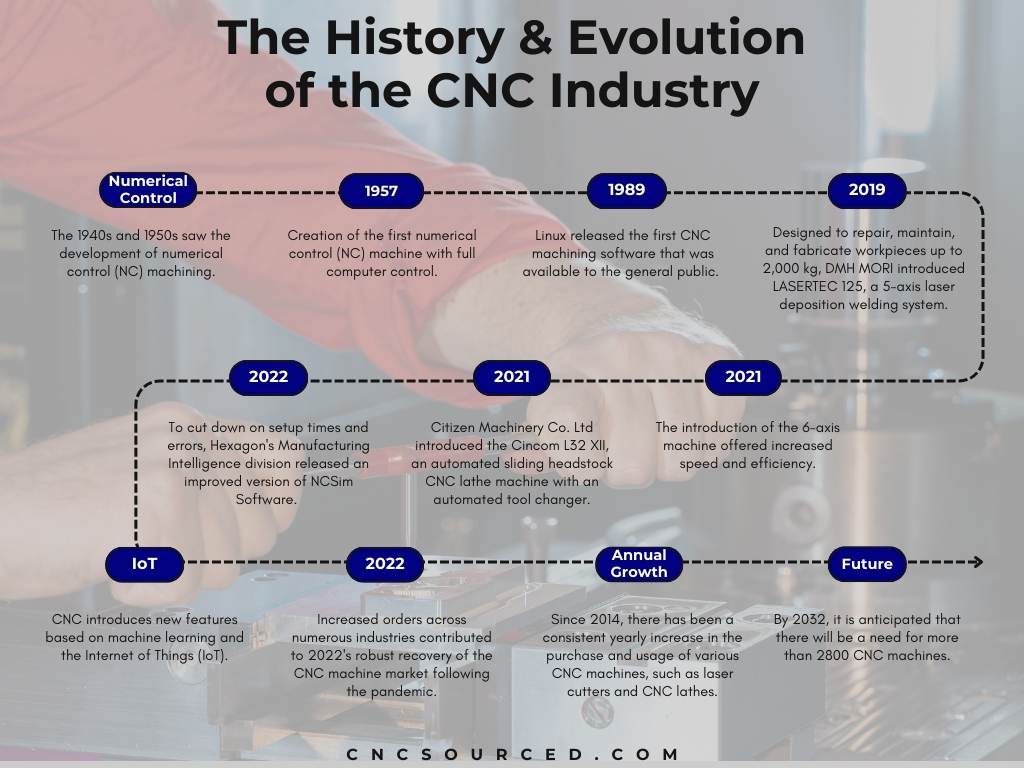
CNC has made impressive gains in its relatively short history. Here’s what you need to know about the key advancements and notable events of the CNC market:
7. Numerical control machining was built in the 1940s and 1950s, and it was used in World War II to make replacement parts for aircrafts. [1]
8. The first fully computer-controlled numerical control machine was developed in 1957. [10]
9. Linux introduced the first publicly available software for CNC machining in 1989. [11]
10. In 2019, DMH MORI launched LASERTEC 125, a 5-axis laser deposition welding system to repair, maintain, and produce workpieces up to 2,000 kg. [3]
11. The 6-axis machine was introduced in 2021, offering improved efficiency and speed. [8]
12. In 2021, Citizen Machinery Co. Ltd introduced the Cincom L32 XII, a sliding headstock automatic CNC lathe machine with an automatic tool changer. [9]
13. In 2022, Hexagon’s Manufacturing Intelligence business unveiled an updated NCSim Software to reduce setup times and errors. [8]
14. The Internet of Things (IoT) and machine learning drive the implementation of new features in CNC. [8]
15. Following the pandemic, the CNC machine market rebounded strongly in 2022 because of increased orders across many sectors. [9]
16. Since 2014, the purchase and use of different kinds of CNC machines, from CNC lathes to laser cutters, have seen continuous annual growth.
CNC Use Cases
CNC machining has shown itself to be extremely beneficial for many industries all over the world. It’s helping automakers, medical device makers, and many other manufacturers save time and money while reducing the risk of human error.
Here are some of the key ways CNC machines are used:
17. CNC is now vital in the automotive industry, responsible for making the majority of elements in modern cars [8]
18. Medical screws, which must be as precise as possible, are nowadays largely made using CNC machining. [2]
19. CNC makes 900 million medical screws each year. [2]
20. CNC machining is used for high-risk ventures like aeronautical engineering, automotive engineering, and military equipment.
21. Europe mainly uses CNC machining for vehicles and factory automation [6]
22. CNC systems are becoming more important in mass-production plants because of their high-precision and cost-reduction properties. [8]
CNC Market Stats
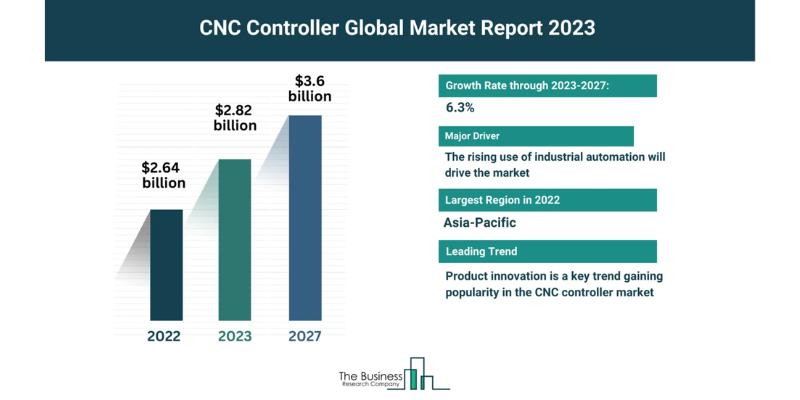
The CNC market is booming, and quickly becoming a worldwide phenomenon in several industries. Here’s a breakdown of the current market size and split:
23. The CNC drilling machine market was worth $1.8 billion in 2022 [7]
24. In 2020, automotive companies accounted for 40% of industry use
25. CNC metal cutting tools are increasingly popular due to their accuracy, speed, and energy efficiency. [3]
26. High-precision engineering is the fastest-growing market segment due to the demand from the defense, medical, and aerospace sectors. [3]
27. One of the largest challenges in the market is a lack of qualified operators, which illustrates a need for training programs. [9]
28. Asia Pacific dominates the CNC market share. [3]
29 CNC machines make up around 89% of the machine tool industry in India. [5]
30. The CNC industry in India grew by $1.9 billion USD in India in recent years [5]
CNC Machines & Software
Lathe machines are on top when it comes to CNC machines, but machines and CAD CAM software only continue to advance.
31. Lathe machines held the largest revenue share (28%) in 2022, a trend that’s expected to continue. [8]
32. Simulation, verification, and optimization software are advancing CNC machinery to reduce scrap and damages, saving firms time and money. [8]
33. A 6-axis CNC machine can reduce cutting time by up to 75% compared to a 5-axis one. [8]
34. The abundance of shop floor sensors facilitates predictive maintenance to keep CNC machines in top working order. [8]
CNC Cost
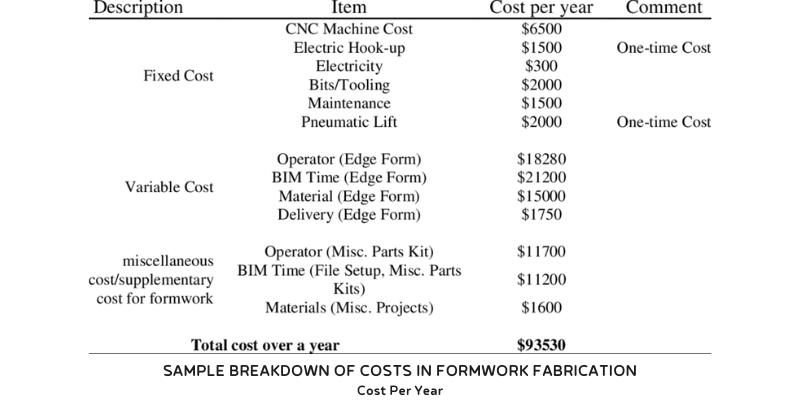
CNC machines will cost a pretty penny, but they can certainly be worth it. Here’s a closer look at the CNC costs:
35. CNC cost more than manually-operated machines, and they require regular maintenance of high-tech pieces. [3]
36. $13800 is the average price for a flatbed CNC lathe. [8]
37. Vertical machining center lathes cost between $20,000 and $22,000 on average. [8]
38. A CNC router machine costs between $9,000 and $10,000. [8]
39. CNC milling machines cost on average between $4,500 and $5,500. [8]
The Future of CNC
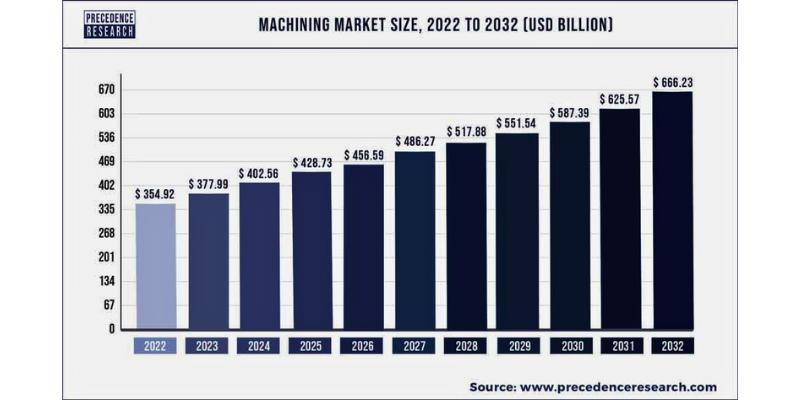
CNC is already making waves in industries including auto, medical, aerospace, and many more. But its potential to streamline and automate manufacturing has just been scraped. Here’s what we can expect for the future of the CNC market:
40. The predicted demand for CNC machines is expected to exceed more than 2800 by 2032. [9]
41. There is expected to be a need for over 600,000 units of CNC laser equipment by 2032.
In coming years, the transport machinery and general machinery segments are predicted to grow. [3]
42. North America is predicted to increase market share as it adopts more advanced technology. [3]
43. The CNC market is predicted to reach over $2.5 billion by 2030. [7]
44. The U.S. CNC machines market is projected to reach $4,009.5 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.9% from 2021 to 2030. [4]
45. The demand for faster machining and lower worker requirements is set to propel the laser machine segment. [8]
46. The industrial sector is anticipated to grow to account for 28 billion market share (holding more than ¼ of all market share). [9]
47. The rise of EVs is also predicted to expand the automotive sector in the CNC industry. [9]
48. Manufacturers are creating hybrid machinery that combines additive and subtractive CNC technology. [3]
The CNC industry adapted after COVID-19 challenges and continues to experience growth due to the demand for automation, precision, and efficiency. Businesses in the medical, automotive, electronic, and aerospace industries will continue to implement CNC technology to improve manufacturing speed and systems.
At the same time, leading CNC machine producers must invest in research and development to implement new technologies that meet these growing needs.
Sources:
- https://www.iridiummanufacturing.com/blog/A-Brief-History-On-CNC-Machinery_AE16.html
- https://www.mmsonline.com/blog/post/medical-screw-solution-includes-more-than-cutting-tools
- https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/computer-numerical-controls-cnc-machine-tools-market-101707
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/us-cnc-machines-market-A13061
- https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20201122005063/en/Machine-Tool-Market-to-Grow-by-1.9-Billion-in-India-COVID-19-Business-Continuity-Plan-Rising-Industrial-Automation-to-Boost-Growth-Technavio
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/europe-computer-numerical-control-cnc-machine-market
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1415067/cnc-drilling-machine-market-size-worldwide/
- https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/cnc-machine-market/126307/
- https://www.precedenceresearch.com/computer-numerical-control-machine-market
- https://www.iridiummanufacturing.com/blog/A-Brief-History-On-CNC-Machinery_AE16.html
- https://www.cncsourced.com/cnc-machining/best-cnc-software-free-professional/