Mechanical engineering is a vast field that covers a range of scales, from nanomechanics at the nanoscale to aerospace at the mega scale. As a result, there are many software packages available for mechanical engineers to learn. While there are currently around 100 mechanical engineering software options, a few of these can accomplish most tasks.
In this article, we will introduce the best software for mechanical engineers in four categories: design software, MBD (model-based definition) software, FEA (finite element analysis) solvers, and pipe stress analysis software.
Best Mechanical Engineering Software – Full Round-Up
Here’s a quick list of the best mechanical engineering software and their verdict:
- Autodesk Inventor and SolidWorks are the most popular and best entry-level mechanical engineering software for small companies or product lines that don’t require complex or sophisticated surface design.
- Fusion 360 is the best software for learning CAD and machining, and is also the best option for small businesses that don’t require physical analysis.
- CATIA and Siemens’ NX are the best mechanical engineering software for large companies and complex products.
- Adams is the best mechanical engineering software for multibody dynamics, simulation, and design testing.
- Nastran is the best and most accurate FEA solver for mechanical analysis.
- Abaqus is the best FEA software for production lines that blend devices from other fields with mechanical parts.
- CAESAR II is the best mechanical engineering software for pipe stress analysis.
Best Mechanical Engineering CAD Software
1. Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is the best CAD software for the price. It’s not advanced mechanical engineering software – however, it’s great for small companies or for learning design.
One of the great benefits of Fusion 360 is its direct modeling capabilities. For example, SolidWorks is far more expensive than Fusion 360, but its direct modeling features are not as good.
Fusion 360’s rendering is good, and can display the mechanism’s motion. Fusion 360 also offers advanced integrated CAM – and it’s also free for students or any personal use. With these features and accessibility, I expect Fusion 360 to rise in popularity in the coming years.
However, Fusion 360 is not the right choice for performing advanced mechanical analysis. We also see that a limited number of small companies use Fusion 360 at the moment, though more small companies may switch to Fusion 360 soon.
At about $545 per year for commercial use, Fusion 360 is the cheapest mechanical engineering software on this list.
2. SolidWorks
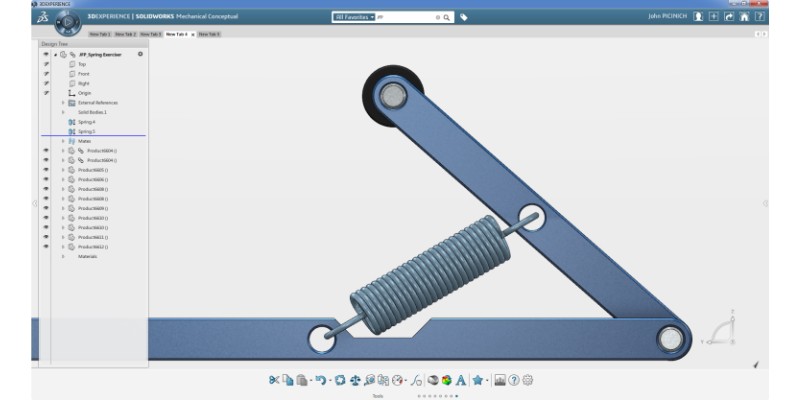
Dassault Systemes’s SolidWorks is the most famous mechanical engineering software. Most mechanical engineers learn SolidWorks, and many industries use it. SolidWorks is user-friendly and easy to learn.
Currently over 70000 companies use SolidWorks, according to Enlyft. This makes SolidWorks the most widely used CAD software in companies around the world. However, large companies tend not to use SolidWorks, as it’s entry-level. Enlyft’s statement that these companies have between 10 to 50 employees verifies this.
SolidWorks offers advanced 3D CAD and a simulator. It also has an assembly environment to fit the various parts together.
Then, SolidWorks can perform a motion study on the machine’s mechanisms. It displays the velocity and acceleration of various points. It can also perform finite element analysis, however, it’s not as sophisticated in this area as the solvers we’ll introduce.
SolidWorks has many add-ons integrating CAM, electromagnetics analysis, full simulation capabilities, and reverse engineering. For example, you’ll unlock its full simulation abilities if you buy its add-on.
SolidWorks costs very little (about $60 per year) if you are a student, artist, or an eligible startup. Otherwise, it costs between $4000 and $8000 based on the plans and features you order. You can also choose its yearly subscription for $2700 to $5000.
3. Autodesk Inventor
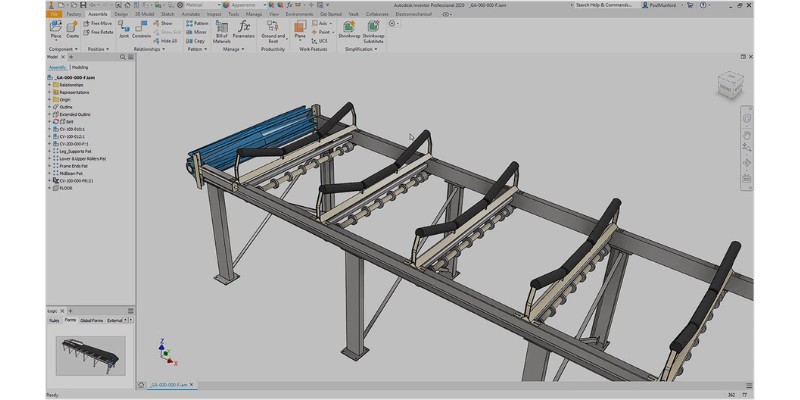
Autodesk Inventor is in the same realm of mechanical engineering software as SolidWorks. It offers professional 3D CAD for industrial designers. It renders simulations well and even works out FEA. Autodesk Inventor is also user-friendly.
At this moment, Autodesk Inventor’s customer list includes 22414 companies. Autodesk Inventor is the second most popular CAD software in the industry after SolidWorks.
For about $2085 a year, Autodesk Inventor is cheaper than SolidWorks. So Inventor can help to keep the costs down when making simple designs.
Although SolidWorks and Inventor have similar capabilities, SolidWorks users say it’s still stronger than Inventor in making a design from scratch. SolidWorks’s simulator is better if your assembly consists of tens of parts. Plus, its workflow is more convenient for industrial design.
4. CATIA
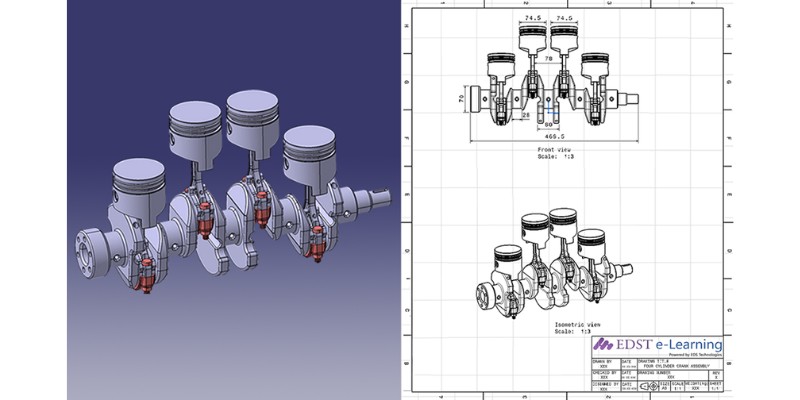
CATIA is another design software from Dassault Systemes, but it’s the more advanced one. It offers professional CAD, assembly, and simulation. None of the software options we’ve covered so far can compete with CATIA in surface design.
Learning CATIA is difficult. That’s why many companies that require CATIA knowledge, still subject their new employees to extensive training.
CATIA can handle large design files, assemble numerous parts, and simulate the motion and physical behavior of various mechanisms.
While SolidWorks manages slightly larger designs than Autodesk Inventor, CATIA handles exponentially larger designs than either of them. Therefore, companies that use CATIA usually build large and complex products.
CATIA is also excellent for surface designs since it has advanced fluid dynamics analysis. Therefore, CATIA is popular among aerospace and automotive designers.
CATIA costs between $9000 and $65000 depending on your needs.
5. Siemens NX
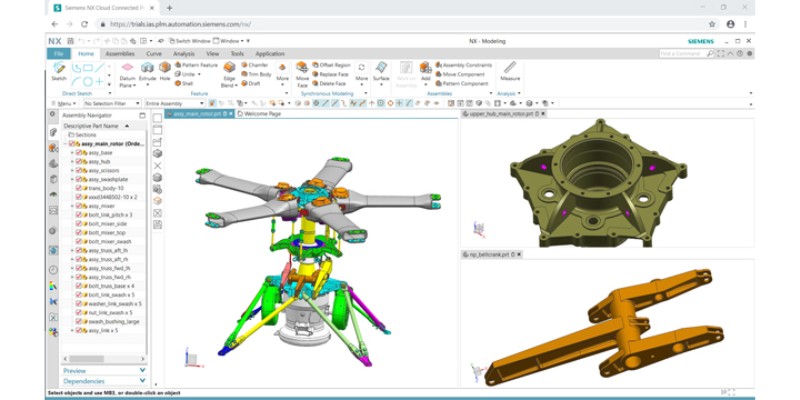
Siemens NX may be the best mechanical engineering software for advanced designs. It’s far more capable and advanced than software like SolidWorks and Inventor, and its surface design capabilities are in CATIA’s class.
However, Siemens NX is far more user-friendly than CATIA. So, Siemens NX blends high-class design capabilities with ease of use and user-friendliness.
Siemens NX has many unique direct modeling tools that a SolidWorks user would never dream of. Siemens has developed these tools and patented them.
Information on how many companies are using Siemens NX is not completely reliable. Although Enlyft has data on 4926 companies using Siemens NX (fewer than CATIA), Infoclutch’s diagrams show that Siemens NX has 12% of the CAD market share (higher than CATIA).
Siemens NX The fact that companies using Siemens NX have between 50 and 200 employees on average, verifies that Siemens NX is in the same class as CATIA.
NX Core Designer costs approximately $3400 per year, and NX Advanced Designer costs about $6900 per year.
MBD Simulators
6. Adams
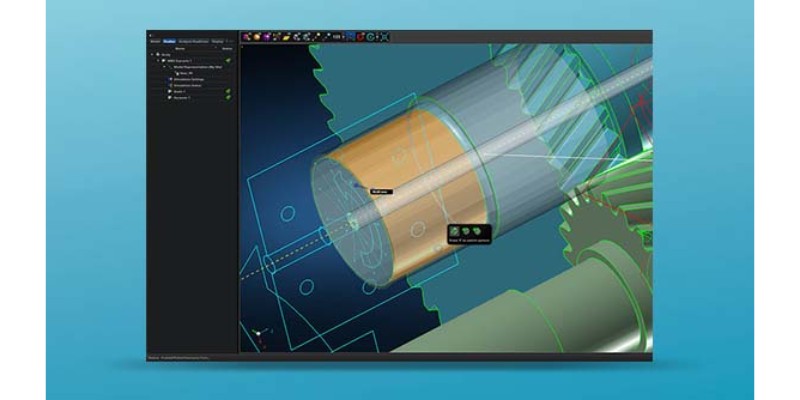
Adams is the best mechanical engineering software in multibody dynamics (MBD). We encounter multibody dynamics when we have many rigid or flexible moving bodies interacting with each other.
While SolidWorks’ motion study toolbox and CATIA’s professional simulations can provide motion analysis, Adams can perform much more advanced and complicated analysis.
Multibody systems interact through motion, structural forces, control systems, actuators, and more. But, it’s important to analyze these systems with real-world physics, rather than ideal models.
For example, consider a multi-body system. How will the forces distribute through the system as the bodies interact with each other? How will shocks affect a mechanism? Is your design optimal for handling the interactions between various bodies?
Where is the weak link in your design chain? Where will your design break first? These are questions that only Adams can answer accurately.
Adams is the software for simulating complicated interactions, like when there are variable moments of inertia and collision.
Adams improves your efficiency because it catches your design mistakes early before you build other components on them. NASA, Overair, and Textron are some of the companies that use Adams.
Although Adams has many CAD features, it’s best to use other CAD software like SolidWorks for your design and import it into ADAMS for MBD analysis.
FEA Solvers
Note that FEA solvers don’t give the same results. Therefore, a trusty FEA solver is a must for every design company.
7. Nastran
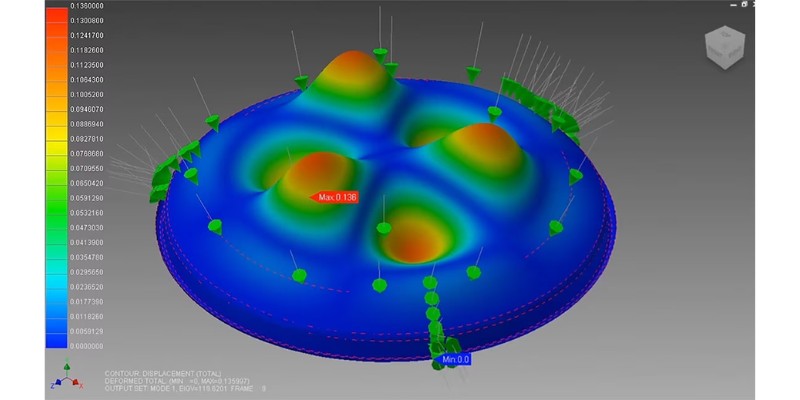
Nastran is the most well-known and widely used finite element analysis solver. Nastran was born in the 1960s to serve NASA to solve its complex problems.
So, it’s no surprise that Nastran is a reliable and accurate FEA solver. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) approves Nastran for finite element analysis of aircraft and airplanes.
It is important to test a design with trusty software like Nastran before building it. Nastran computes the stress in all parts of the design and performs an accurate vibrational analysis. Therefore, most aircraft and car companies use Nastran to analyze their designs.
Nastran is not one software; it’s a solver that you can find in many software. For example, MSC Nastran, Autodesk Nastran, NX Nastran, Inventor Nastran, and many other Nastrans are available.
As you can see, some famous CAD names like Autodesk or NX have facilitated a Nastran solver to integrate with their CAD.
8. Abaqus
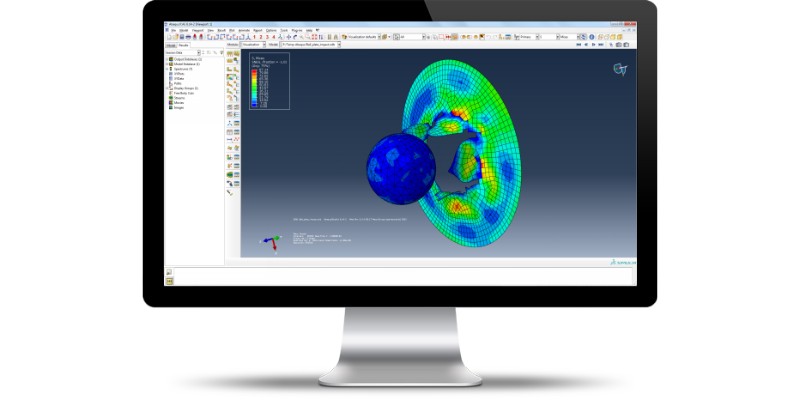
Abaqus is from the same company that makes CATIA and SolidWorks: Dassault Systemes’s Abaqus is their FEA and multiphysics solver.
Abaqus is not as popular as Nastran among scientists and universities. However, Abaqus is well-liked in many industries. Engineers in the production lines like Abaqus since its multiphysics capabilities allow them to work with production components.
Plus, Abaqus has a variety of materials and even allows you to define a nonlinear material. It can solve nonlinear problems, and even provide explicit solutions (if any exist).
9. CAESAR II: The Best Pipe Stress Analysis Software
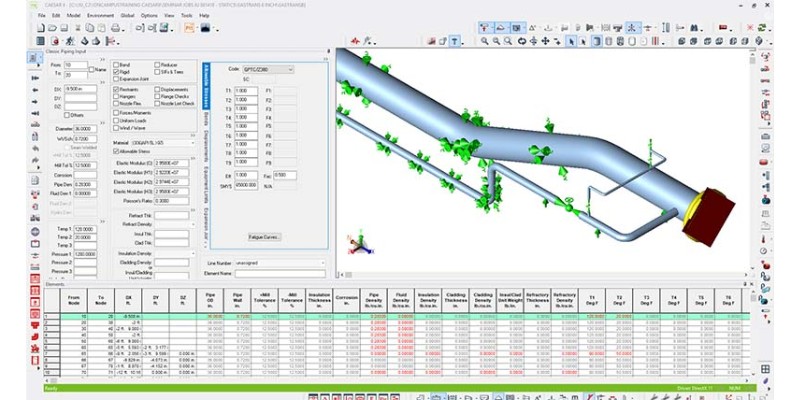
CAESAR II is the best mechanical engineering software for pipe stress analysis. CAESAR II has all the major piping codes (more than 35 international codes) and is the industry standard in piping design.
You can import CAD (piping) files into CAESAR II for analysis. CAESAR II can handle projects of any size.
CAESAR II calculates static stress and gives graphical and numerical recommendations. It also has tremendous dynamic analysis capabilities. It can calculate natural frequencies and analyze the shock spectrum.
CAESAR II is interactive and allows you to walk around your model. It can also animate the dynamic response.
What Can You Expect From Mechanical Engineering Software?
Mechanical engineering software designs, analyzes, and simulates mechanical systems. Engineers use these tools to create detailed designs, perform simulations to test the behavior of a design under different conditions, and analyze the results to ensure that the design meets the required specifications.
Common mechanical engineering software applications include designing and simulating automotive systems, aircraft structures, and medical devices.
What Type of Software Do Mechanical Engineers Use?
Mechanical engineers use several types of software: CAD, CAE, simulation software, solvers, fluid simulation software, CNC and machining software, pipe stress analyzers, pressure vessel design, and heat exchange software. Most mechanical engineering software packages integrate several items on this list.
What Should You Expect From Mechanical Engineering CAD?
Some mechanical engineers use software to design parts, machinery components, and assemblies. 3D CAD and simulation software like CATIA and Autodesk Inventor serve these purposes.
Good mechanical engineering CAD can assemble all the CAD parts together to build the machine.
Then, the software performs the motion study for the mechanical engineer. For example, how the machine moves if a particular motor rotates at 50 RPM.
Mechanical engineering CAD packages are 3D and usually come with simulators and solvers. However, some mechanical engineering software may have separate simulation add-ons.
What Do Solvers Do for Mechanical Engineers?
When you’re studying mechanics in school, you face simple problems to solve with pen and paper. However, designing a machine involves many variables or mathematical problems that don’t have simple solutions (the technical term is closed-form solutions).
That’s when mechanical engineering software comes to the rescue. We rely on mechanical engineering software to perform finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Nastran, Abaqus, and ANSYS are the most well-known software in this area.
A mechanical engineer uses this software to turn his model into a mesh, and then investigate how the model responds to forces and constraints.
Where Can a Mechanical Engineer Work?
Mechanical engineers work in numerous fields and places. Most mechanical engineers work in offices, while others work on job sites to maintain and operate machinery. In short, mechanical engineers work on these projects: airplanes, satellites, UAVs, biomedical devices, military, automation, manufacturing, product design, oceanic infrastructures, cars, ships, trains, submarines, oil and gas, tanks, compressors, and piping.
Aerospace engineers design and build aircraft, UAVs, and anything that flies. Aerospace engineering combines the mechanics of solids, fluids, and control. Some also work for the military.
Control and mechatronics engineers work on automated mechanical systems with electronic parts, motors, or CPUs. These engineers work on robots, UAVs, satellites, and automated mechanical systems.
Mechanical engineers may also minor in medical engineering to design and build appliances for use in the medical field.
Ocean Science engineers build structures in water. These include ocean floor drilling machines, oil structures, ships, submarines, and more.
Some mechanical engineers work in manufacturing. They design appliances, gears, and parts.
Or, they can work in the automotive industry to design cars. Some mechanical engineers also become railway engineers. They design trains and traffic control systems.
Some mechanical engineers work in the oil and gas industry, port facilities, and petrochemicals. They design storage tanks and piping systems.
On the other hand, field mechanical engineers work on-site to operate and maintain mechanical machinery. These engineers work on ships, in factories, oil structures, and other mechanical facilities.
Will Mechanical Engineers Become Obsolete?
No. Mechanical engineers remain in trend as long as humans make things that move. Mechanical engineers design anything that flies, sails, or orbits, and none of these are becoming obsolete. Mechanical engineering has also progressed to other fields like biomedical engineering, and nanomechanics. We’ll also need mechanical engineers to design cars and other products.
How Is Mechanical Engineering Similar to Software Engineering?
Mechanical and software engineers spend a lot of time behind computers. Usually, both mechanical and software engineers are part of a team that breaks a project into many pieces. Therefore, they both need problem-solving skills while seeing their role in the project’s bigger scheme. Also, mechanical, electrical, and software engineers may work alongside each other in robotics.
Can Mechanical Engineers Be Software Engineers?
Yes, mechanical engineers can become programmers for three purposes. A handful of mechanical engineers learn programming to develop mechanical engineering software. Some mechatronics engineers learn programming to write codes for the movements of robots or automated moving objects. Finally, like everyone else, mechanical engineers can also become software engineers by changing their field.
Which AutoCAD Version Is Best for Mechanical Engineering?
AutoCAD (full version) is better than AutoCAD LT for mechanical engineering since it includes AutoCAD Mechanical. However, AutoCAD is not Autodesk’s most advanced software for mechanical engineers. Autodesk Inventor and Fusion 360 are far more capable than AutoCAD for creating mechanical parts and assemblies. They also have better 3D and simulation capabilities than AutoCAD.
Related articles:
- Top 9 Best CNC Simulator Software 2022 (Free & Paid)
- CNC Programming: A Complete Beginner’s Intro (Guide)
- Best CNC software for CAD CAM
- Best free CNC software for CAD CAM
- Best design software for cabinets
- Best woodworking CAD software
- The best free PCB design software
- The best parametric modeling software