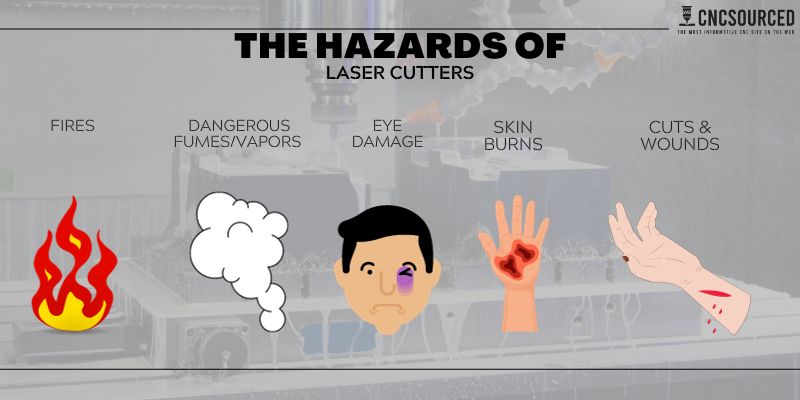
Key Takeaways
- Fire Hazard: Laser cutters can ignite flammable materials and cause fires. Use only laser-safe materials and supervise the machine.
- Toxic Fumes: Laser cutters can produce harmful gases from some materials. Use exhaust systems, air filters, and good ventilation.
- Eye Damage: Laser cutters can damage the retina and cause vision impairment. Wear safety glasses and avoid direct or reflected laser beams.
- Skin Burns: Laser cutters can burn the skin with high-energy light. Wear protective gloves and clothing and avoid contact with the laser.
It’s very important to remember that laser cutters can be extremely dangerous if laser safety rules are not followed.
If you are a first-time user of laser cutters, it’s essential that you’re aware of cutting hazards and cutting safety precautions associated with laser cutting.
- Key Takeaways
- Why can lasers be dangerous?
- Laser cutter hazards
- How to Safely Use Laser Cutters – 9 Tips
- 1. Don’t leave an operating system unattended
- 2. Keep the laser away from debris
- 3. Avoid direct eye contact with the laser
- 4. Use safe materials only
- 5. Never disable the safety features on the laser machine
- 6. Manage the laser heat with good cooling
- 7. Use the correct laser settings
- 8. Use air assist
- 9. Stay alert
- FAQs
- Final Thoughts
Potential hazards include:
So to stay safe while laser cutting, it’s important to:
- Not leave your laser unattended
- Keep the laser away from debris
- Avoid direct eye contact with the laser
- Use compatible materials only
- Don’t disable any safety features
- Use the correct cooling
- Use the correct laser settings
- Use air assist
- Stay alert
Read on below to find out more about the risks of laser cutters, dangers, hazards, laser cutter safety, and more.
Why can lasers be dangerous?
Before getting stuck into the hazards, let’s briefly recap how they work, and why this makes them dangerous:
Laser cutters use a focused beam of light to cut through various materials such as wood, plastic, and metal. The high-energy beam is so concentrated that it can vaporize the material, which also makes the laser dangerous.
Laser cutter hazards
Laser safety risks commonly result from laser beams that have not been contained, poor ventilation systems, or the use of flammable materials.
The most common laser cutter hazards include the following:
1. Fires
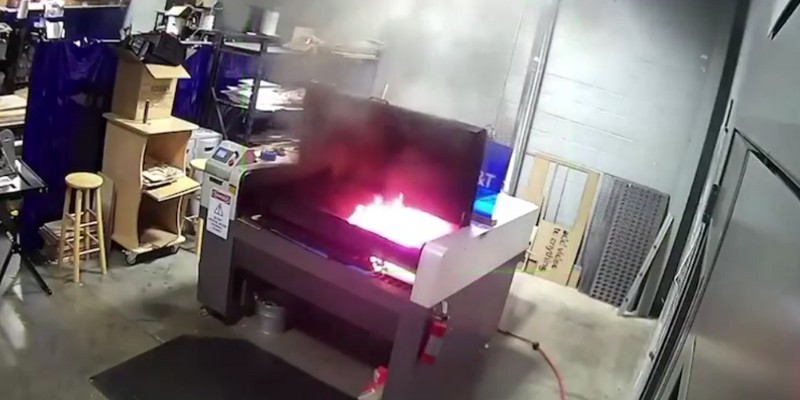

Laser cutters can cause fires if the material being cut is flammable or combustible. If the laser’s energy is not properly controlled, the laser beam can ignite the material and any other combustible in close proximity.
This is why it is essential to use only laser cutter-safe materials on a laser bed to avoid a fire hazard. Also, you need to take special measures for some materials. Some materials, like PVC, produce flammable fumes when burned and therefore shouldn’t be laser cut.
2. Dangerous fumes/vapors

When laser cut, some materials can emit laser-generated air contaminants (LGACs), which are harmful gases that can pose serious health risks when inhaled.
For example, PVC releases toxic gases (including chlorine) when lasered, which is highly corrosive and dangerous. You should never laser cut PVC.
To mitigate the risk of exposure to LGACs, be sure to use exhaust systems and air filters to capture and remove laser dust and fumes from the air. Also, good ventilation in your workspace is essential.
3. Eye damage
Eye damage can occur when a laser beam enters the eye and damages the retina. This can lead to retina damage, cataract, and cornea damage, depending on the wavelength. The more powerful the laser, the more dangerous it is.
It’s vital to know that eye damage from lasers is not just the result of direct eye contact with the laser beam. In Class 3B and Class 4 lasers, the beam is so powerful that its reflection from surfaces can enter the eye and damage it.
So, when working with these lasers, you must to wear laser safety glasses at all times.
It’s also crucial to make sure your laser is properly contained, and that all the laser’s safety features are functional. This includes interlocks that turn off the laser when the machine’s door or cover is open.
4. Skin burns
Laser cutters can cause severe skin burns when the laser’s high-energy light comes into contact with the skin, heating it to the point of damage or combustion.
The risk of skin burns is greater with more powerful lasers, and certain wavelengths that the skin better absorbs.
5. Cuts and wounds
Laser cutters can cause puncture wounds when a user accidentally comes into contact with the sharp or pointed edges of the material being cut or the moving parts of the laser cutter itself.
While not directly related to the laser beam itself, laser cutting can create sharp or pointed edges on the material. These can potentially cause cuts or puncture wounds.
To prevent these accidents, it’s important to handle the cut materials with care, especially immediately after cutting, when edges can be particularly sharp.
Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, such as cut-resistant gloves, provides extra protection. Also, users should always be mindful of the machine’s moving parts and keep their hands and fingers clear when the machine is operating.
How to Safely Use Laser Cutters – 9 Tips
Users should always practice laser safety every time they operate the machine. A few safety precautions are listed below:
1. Don’t leave an operating system unattended
Leaving laser cutters unattended during operation risks a fire breaking out from the laser igniting the material being cut. This risk is especially high if the material is flammable or you’re using the wrong laser settings.

Therefore, it’s key to always supervise a laser cutter while it’s operating, and to have fire safety measures in place, such as a nearby fire extinguisher.
2. Keep the laser away from debris
When laser dust and debris accumulate around the laser cutter, they pose a serious fire hazard. These particles can ignite if they come into contact with the laser beam or the heat it generates.
This debris can also affect the machine’s operation and potentially cause damage or wear.
Therefore, it’s important to regularly clean your workspace and your machine itself, especially the cutting bed and the area around the laser. This’ll also improve your laser’s longevity and better maintain performance.
An efficient exhaust system also helps remove dust and fumes from the cutting area, improving air quality when working and reducing fire risk.
3. Avoid direct eye contact with the laser
Eye contact with a laser-cutting beam can cause damage to the sensitive tissues of the eye. Even brief exposure to the laser beam can cause temporary vision impairment.
You must always practice laser safety by wearing safety glasses when operating your laser cutter.
4. Use safe materials only
Before using any material on a laser cutting machine, it is recommended to consult the machine’s manual and guidelines to ensure that the material is safe and suitable.
Materials that are safe to use generally include wood, plastics/acrylics, and metal. Materials that are not safe to use include:
- PVC – releases harmful chlorine gas
- Vinyl – releases harmful chlorine gas
- Polystyrene and Polypropylene foam – very flammable
- Fiberglass – releases harmful gases
- Polycarbonate – doesn’t cut well and can release harmful fumes
- Carbon fiber (if coated) – releases harmful gases
5. Never disable the safety features on the laser machine
Never disable laser interlocks built into the cutter. Interlocks are designed to shut off the laser if the cover or door of the machine is opened during operation. Disabling them could result in skin burns, eye damage, and other physical health risks.
6. Manage the laser heat with good cooling
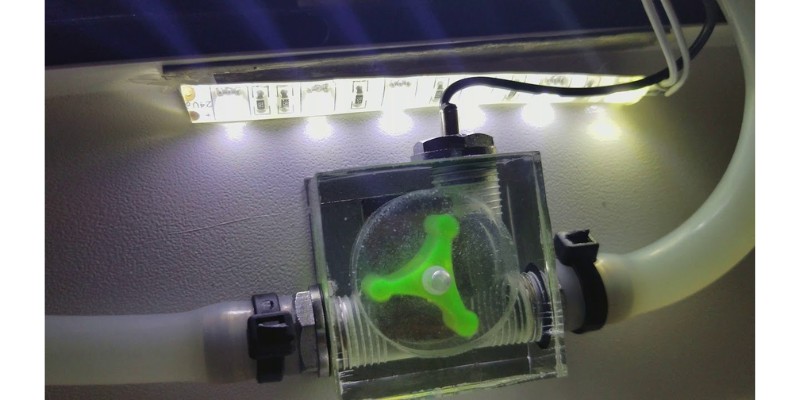
A laser cutting machine will be at a greater risk of overheating and malfunctioning if it is used in a hot environment, and usually need cooling to stay safe.
Laser cutters need to be operated with adequate ventilation and heat management. Some laser cutters have built-in cooling systems (like water cooling for the laser tube in CO2 laser cutters) to prevent overheating.
However, in the same way, being too cold can also cause issues. For instance, if a water-cooled laser tube freezes, it could crack.
7. Use the correct laser settings
Many compatible laser materials can also be fire hazards. For example, cardboard, paper, and wood are great for laser cutting, but using too much power at low speeds can set them on fire.
8. Use air assist
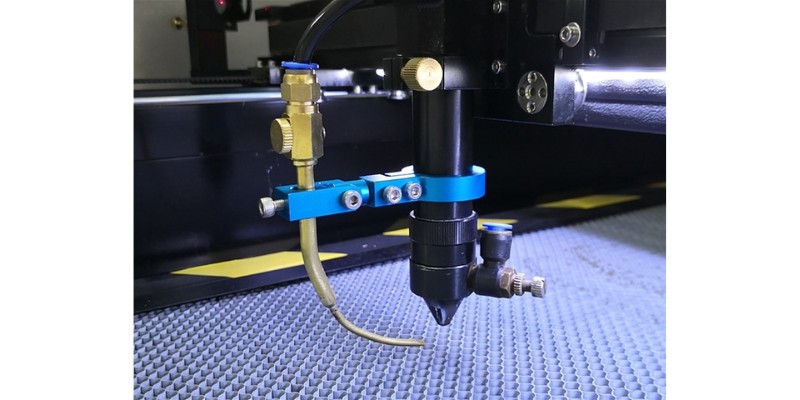
Using air assist greatly reduces the chance of fire, by blowing heat away to prevent any combustion from the gases generated during cutting.
Many CO2 lasers come with air assist nowadays, but lower-cost diode laser engravers sometimes do not.
For me personally, I bought my own air assist upgrade for my Ortur Laser Master 3, and I bought xTool’s air assist for my xTool D1 Pro.

9. Stay alert
Always stay alert when operating the machine. Accidents can happen when users become too complacent and forget to be careful. By keeping focused on the task at hand, accidents can be avoided. And make sure to not leave your laser unattended for long periods of time.
FAQs
What materials should not be cut with a laser cutter?
A few materials that should never be cut with a laser cutter include PVC, fiberglass, polycarbonate, carbon fiber, and coated materials.
How hot is a laser cutter?
The temperature of a laser cutter can vary depending on the type of laser and the material being cut. When cutting metal, the temperature can reach up to 3000°C, while cutting wood or plastic may reach temperatures up to 500°C.
Are laser cutters safe to use at home?
It is safe to use a laser cutter at home if you follow a safe operating procedure. Users should also always be aware of how to prevent laser hazards by wearing protective gear, avoiding direct eye contact with the laser, and using laser cutter-safe materials only.
Are laser cutter fumes toxic?
The fumes produced by laser cutters can be toxic and potentially harmful. However, this depends on the type of material being cut and the ventilation system in place.
Final Thoughts
While laser cutters are a very useful tool in many industries, they can be dangerous if laser safety practices are not followed. Users should always abide by the safety features and take care to avoid hazards such as fires, dangerous fumes, eye damage, and more.