You can make all sorts of different projects by laser cutting and engraving wood. However, some woods are better suited to laser cutting than others, and some should be avoided altogether.
To help you find the right wood for your project, in this guide I’ll reveal the best wood for laser cutting and engraving. We’ll explore different types of hardwood and softwood that can be used for all sorts of different projects, from small crafts to musical instruments.
Generally, birch, maple, and cherry are the best woods for beginners to use.
Best Wood For Laser Cutting & Engraving – Full Round-Up
Best Softwood
- Balsa: For thermal and sound insulation, crafts like model airplanes, fishing floats, surfboards, and musical instruments
- Redwood: For carving small crafts and decorations and musical instruments
- Cedar: For outdoor furniture and fencing
- Cork: For personalized coasters and even wine bottle labels
- Pine: For furniture and joinery to coasters, personalized keyrings, picture frames, and small signs
- Yew: For bench or chair and archery bows
Best Hardwoods
- Birch: For brace and structural component in carpentry
- Cherry: For both small crafts and larger products such as furniture
- Maple: For 3D wood carving
- Basswood:
- Poplar: For wooden toys, crafts, and models, as well as for larger products like cabinets
- Mahogany: For premium furniture, musical instruments, decorations and ornaments
- Walnut: For wood sculptures
- Oak: For laser engraving and projects like joinery
- Ash: For laser engraving tennis rackets and baseball bats
- Alder: For decorative wood products
Best Engineered Woods
- Plywood: For effective and accurate cutting
- Particleboard: For all sorts of laser projects
Best Softwood For Laser Cutting
Balsa, pine, cedar, and redwood are some of the most popular softwoods for laser cutting and engraving projects.
Balsa
- Best for: thermal and sound insulation, crafts like model airplanes, fishing floats, surfboards, and musical instruments
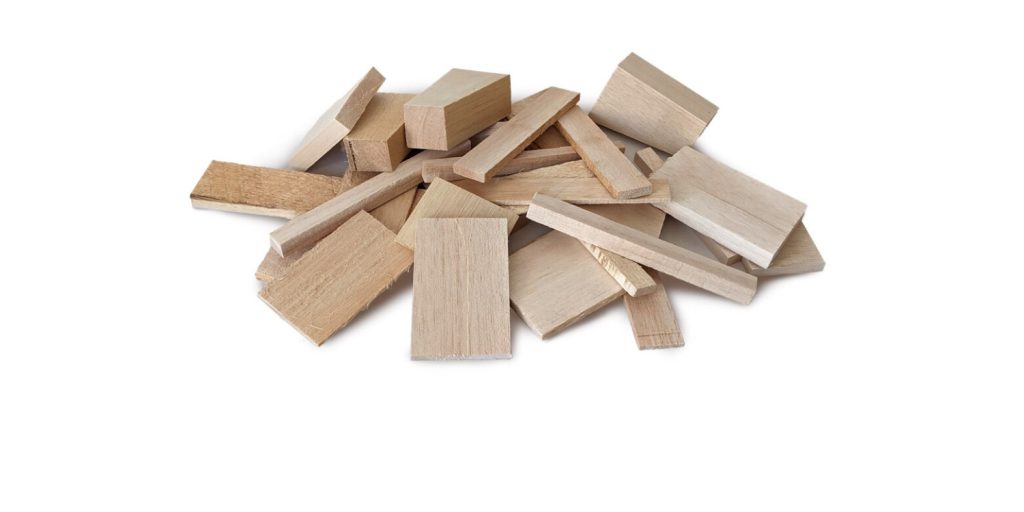

Balsa is one of the lightest woods, and can vary in color from pale white to reddish-brown. As it has straight grains and a low density, balsa is one of the easiest woods to laser cut and engrave. It’s also one of the cheapest woods you can buy.
The low grain density also helps you achieve precise cutting while producing little fumes. Balsa wood has a wide range of uses, including thermal and sound insulation, crafts like model airplanes, fishing floats, surfboards, and musical instruments.
It’s often regarded as one of the best wood to laser cut craft projects due to its easy availability, low price, ease of cutting, lightweight, and the fact it stains and finishes well.
Redwood
- Best for: carving small crafts and decorations and musical instruments
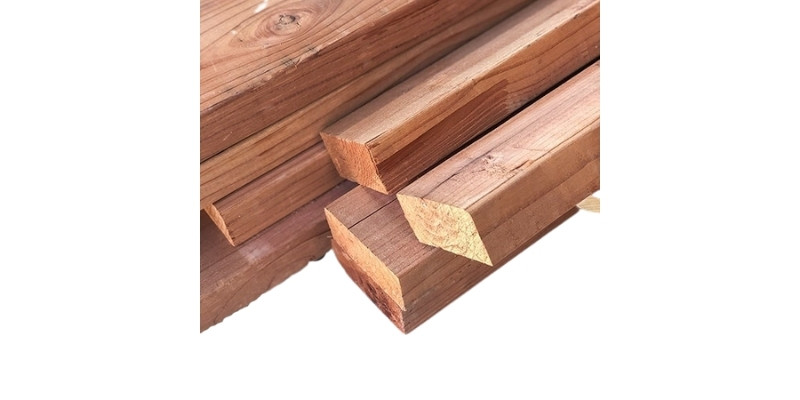

Redwood is quite a soft wood that can range from yellow to pinkish to red in coloring. So, you can achieve different effects and coloring with laser engraving depending on the shade of your workpiece.
Redwood’s softness makes it a popular choice for carving small crafts and decorations, although it’s also a popular choice in musical instruments, so you could use it to finish a CNC-cut guitar, for example.
Cedar
- Best for: outdoor furniture and fencing
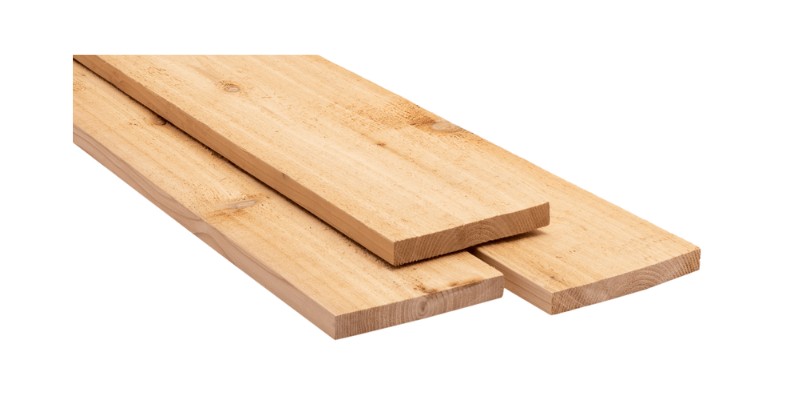

Cedar is a popular wood for laser cutting products due to its reddish coloring and pleasant aroma. It also has fantastic weather resistance and is a popular choice for outdoor furniture and fencing.
Cedar is a fairly knotty wood that gives cedar projects a nice aesthetic appearance. It’s one of the denser softwoods and offers good strength.
Cork
- Best for: personalized coasters and even wine bottle labels
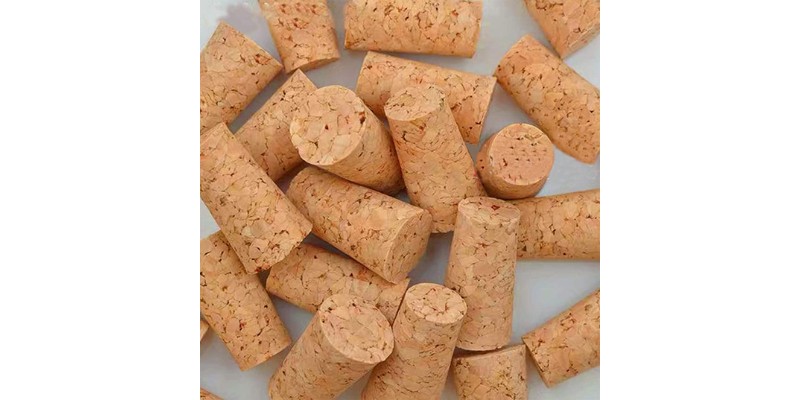

Cork itself isn’t technically a wood. It’s a material derived from the cork oak tree, which is native to parts of Southern Europe and North Africa.
The benefit of cork for laser cutting is that it’s very soft and easy to cut, as well as being super cheap. You can easily buy cork boards from Amazon and other sites, which you can use to make personalized coasters and even wine bottle labels.
Pine
- Best for: furniture and joinery to coasters, personalized keyrings, picture frames, and small signs
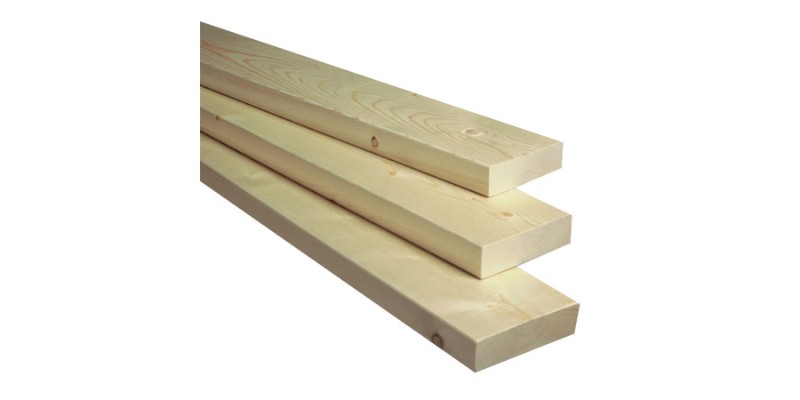

Pine varies in strength and hardness depending on the species, with the likes of red pine and spruce pine being harder than white pine and sugar pine.
Despite the differences in strength, pine typically has a light pale color with straight grains, which makes it a good blank canvas for laser engraving designs. Some people have even created laser engraved portraits on pinewood. You can produce brown lines when engraving and blacker colors by cutting.
Pine’s attractive grain and medium-to-coarse texture make it a popular choice for all sorts of projects, from furniture and joinery to coasters, personalized keyrings, picture frames, and small signs.
Yew
- Best for: bench or chair and archery bows
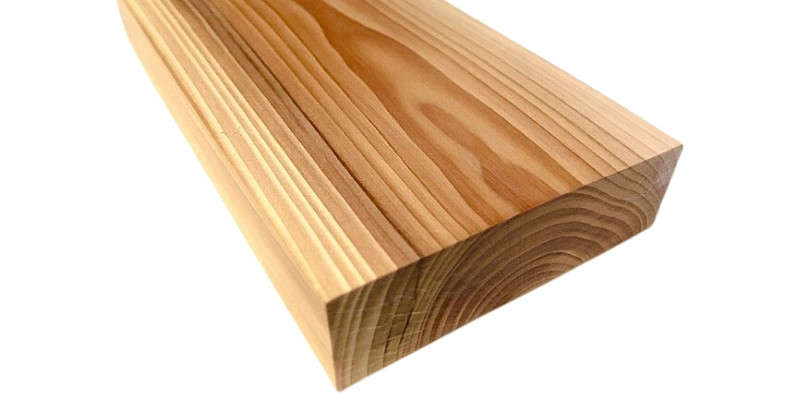

Yew is among the hardest softwoods, and is also expensive and not easily available. However, it’s often sought after due to the stunning aesthetic produced by its wavy grains and knotting, which look particularly beautiful when finished.
Laser engraving on yew will typically provide a dark contrast. Like cedar, it would be a good choice if you wanted to laser engrave a bench or chair, for example.
Yew also has one of the more unique applications among woods, as its elasticity makes it a popular choice for archery bows.
Best Hardwoods For Laser Cutting
These include basswood, popular, walnut, oak, and mahogany.
Whereas softwoods are from coniferous trees, hardwoods are from deciduous species. Some live up to the name by being extremely hard, while others are a lot softer.
Birch
- Best for: brace and structural component in carpentry
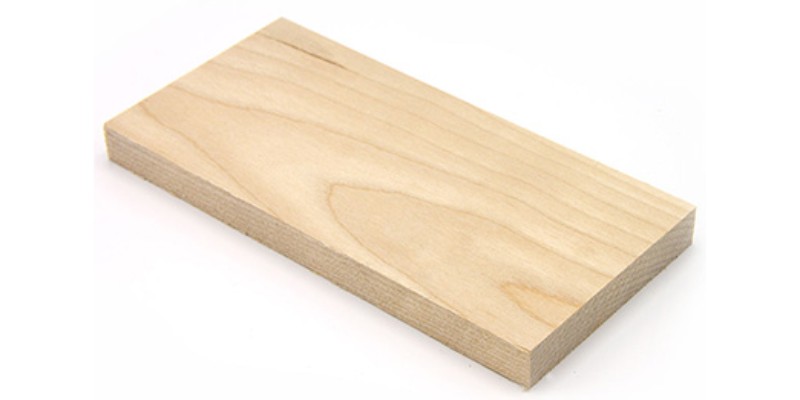

Birch is a stiff hardwood that’s very cheap and easily available. It has a light coloring, making it a good canvas for producing different laser engraved effects.
Birch is typically sold in plywood form, which is smooth and has uniform, loosely packed grains, helping achieve accurate cuts in a single pass.
Cherry
- Best for: both small crafts and larger products such as furniture
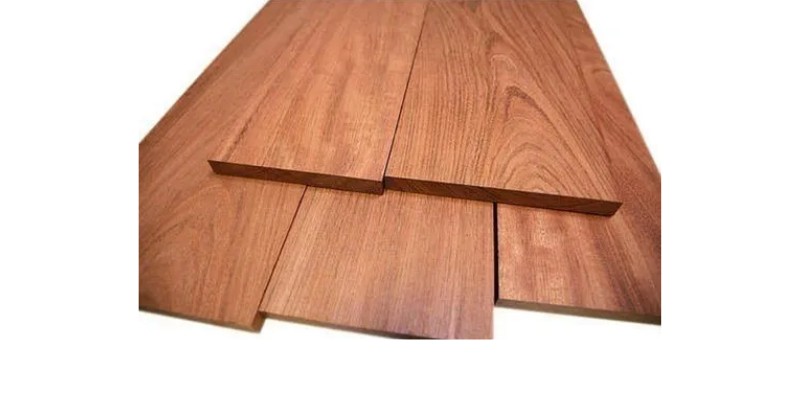

Considered one of the most beautiful woods, cherry can range in color from reddish, to brown, to pale yellow, producing a highlighted effect when engraved and deeper brownish cut marks.
One of the softer hardwoods, cherry is generally easy to work with and is a popular choice for both small crafts and larger products such as furniture.
Maple
- Best for: For 3D wood carving
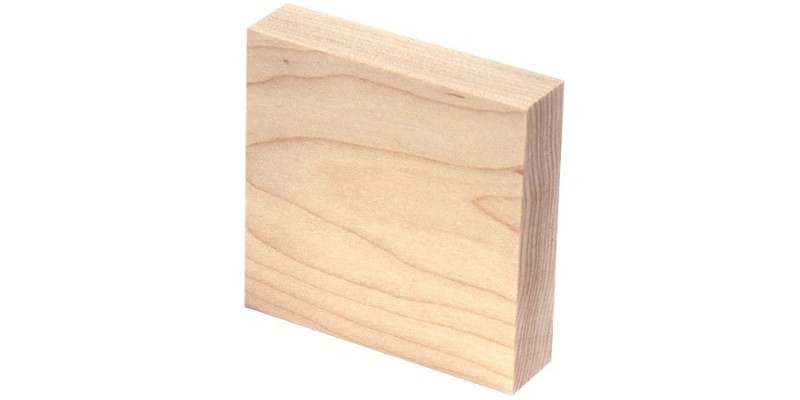

Maple is often favored for its appearance with reddish to golden tones and it typically burns very dark when laser cut.
It has an attractive texture with fine grains and is easy to work with, and it also finishes great.
Basswood
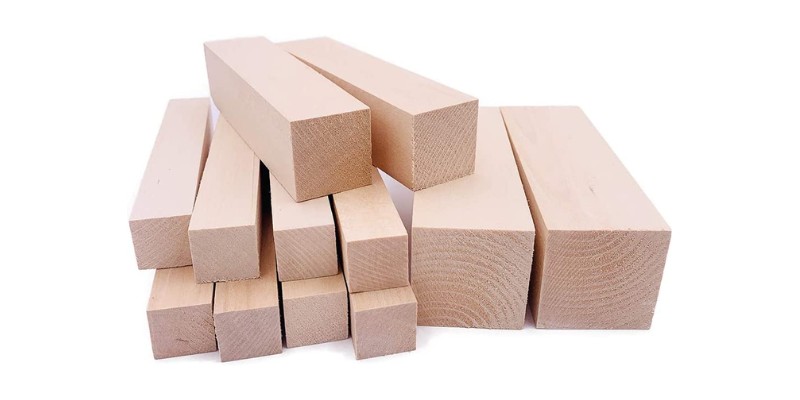

Basswood is a light-colored and soft hardwood with a fine, even texture that makes it very easy to work with. Its low density means you can cut it with a weaker laser than other hardwoods, and its pale tones allow you to produce various colored effects by engraving and cutting.
Basswood is much cheaper than most other hardwoods and is widely available; you can buy blocks easily from Amazon and other sites.
Poplar
- Best for: wooden toys, crafts, and models, as well as for larger products like cabinets
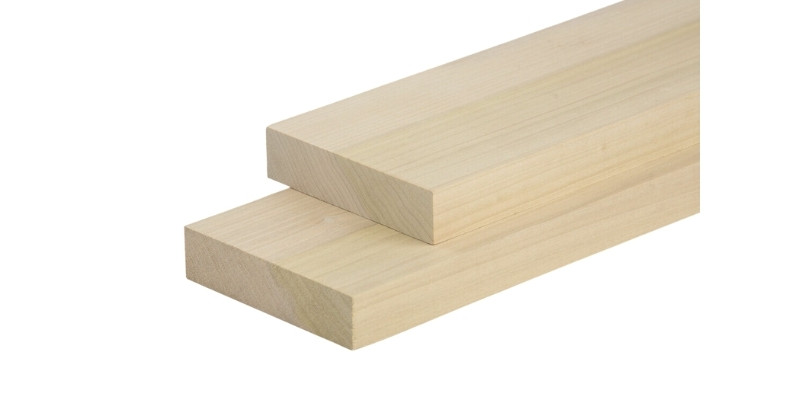

Like basswood, poplar is actually pretty soft, so it can be smoothly cut without needing a hugely powerful laser. Its color can vary between white, yellow, and brown. Engravings usually produce a brown color, while cutting poplar gives a darker, blackish border on the cut lines.
A cheap and easily available wood, poplar is commonly used for making wooden toys, crafts, and models, as well as for larger products like cabinets.
Poplar is one of the most smoke-producing woods when laser cutting, so you’ll need a suitable extractor.
Mahogany
- Best for: premium furniture, musical instruments, decorations and ornaments
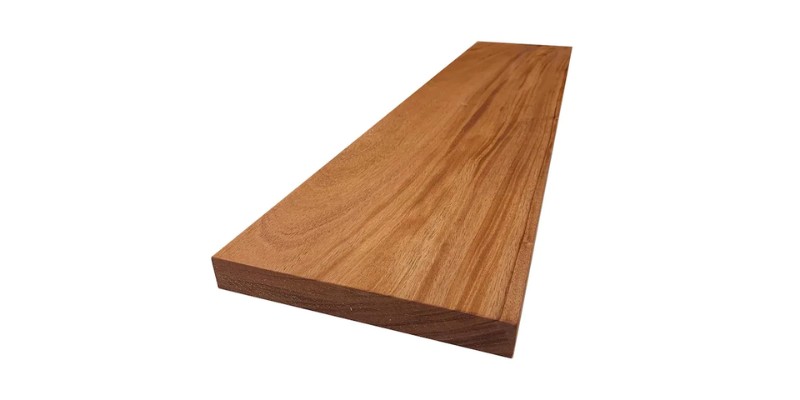

Arguably the best laser cutting wood for luxury products, mahogany is widely regarded as the most premium wood due to its stunning appearance, and is also among the most expensive.
It’s best known for its use in premium furniture, but can be used for all sorts of different projects, from musical instruments to decorations and ornaments.
Mahogany’s beautiful aesthetic makes it a great choice for laser engraved jewelry boxes and similar products. Due to its dark appearance, you will need a powerful laser to make deep engravings so you can get a nice and easily visible contrast.
Walnut
- Best for: wood sculptures
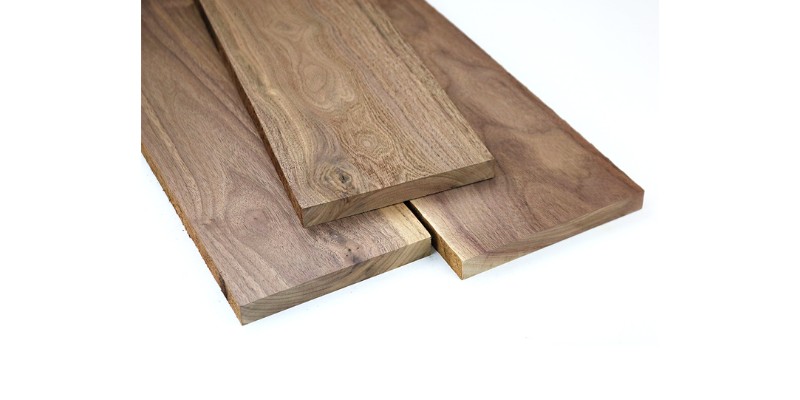

Walnut is often favored for its rich, dark brown, almost chocolatey appearance, although there are also lighter variations. It’s a very strong wood similar to mahogany, and is also one of the pricier options.
One of the benefits of walnut for laser cutting projects is that its straight grains make it easy to cut thin slabs, so it’s perfect for things like personalized cutting boards. It’s also shock and burn resistant, making it one of the go-to materials for wood sculptures.
Shallow engravings on walnut usually produce a highlighted effect, while going deeper brings out an almost black effect.
Oak
- Best for: laser engraving and projects like joinery
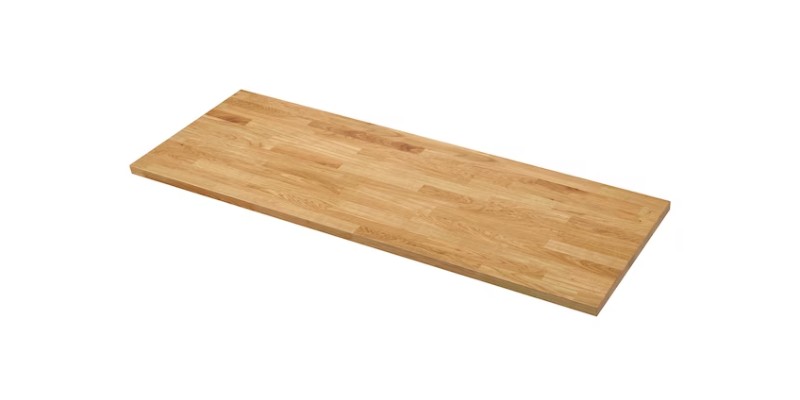

Oak is one of the hardest woods and typically has a yellowish-brown color, although there’s also red oak which has a reddish tint. Its densely packed grains result in fantastic durability, and it’s often favored for projects like joinery due to its distinctive ring pattern.
You typically get a dark contrast when laser engraving oak. It also stains well, so the base wood can be stained in different shades depending on what you want to make and what coloring you want to produce with your laser.
Oak is also popular due to its fragrance, which varies between species and depending on the quality of the wood. Generally, oak is one of the more affordable hardwoods. It’s sometimes considered the best wood for laser engraving for its mix of strength, coloring effects, and affordability.
Ash
- Best for: laser engraving tennis rackets and baseball bats
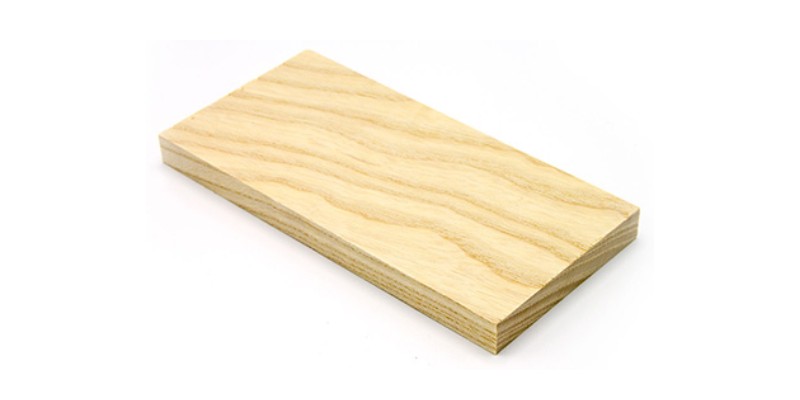

Ash is among the strongest, stiffest, and most durable of all hardwoods. Not only that, but it also has a unique level of elasticity along with great shock resistance, which makes it arguably the best wood for laser engraving sports products such as tennis rackets and baseball bats.
It’s also used in drum casings, for wooden tool handles, and, along with yew, is one of the most common choices for archery bows.
Ash typically has a light yellow color and so you can produce sharp contrasts with laser cuts and engravings. Bear in mind that, like oak, ash requires a powerful laser and is best cut at lower speeds than software woods.
Alder
- Best for: decorative wood products

Alder has a darker, richer color than most other woods and a straight, uniform grain arrangement. This makes it a popular choice in decorative wood products, as you can produce dark burn colorings with laser cutting and
It’s also one of the softer hardwoods, which makes it easier to work with than the likes of oak and ash. It’s also not particularly expensive, so it’s a good alternative to the likes of walnut and mahogany.
Best Engineered Woods For Laser Cutting
Engineered woods are products typically made of wood pieces, chips, or residue, bound together with a synthetic resin.
They have the benefit of good strength while being cheaper than real wood. Although some engineered woods like MDF aren’t ideal for laser cutting, plywood and particleboard are two options to consider.
Plywood
- Best for: effective and accurate cutting
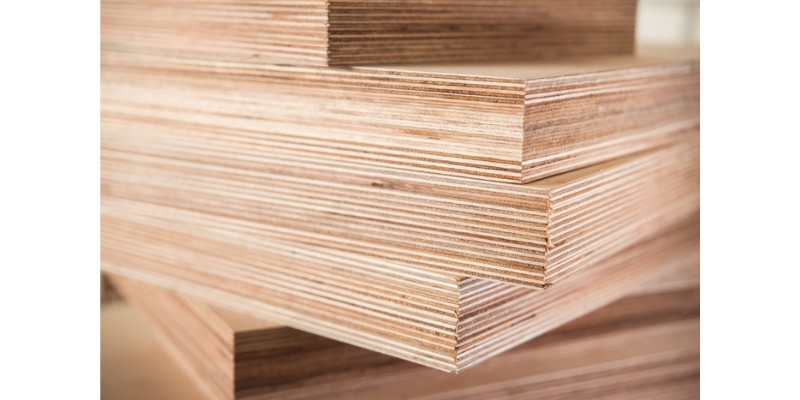

Plywood is made up of thin sheets of wood that are glued together. Due to the presence of glue, you need to use plywood that’s specifically designed for laser work, rather than any common type of plywood.
Laser plywood is widely available online, typically made of birch but sometimes also other species, such as poplar. The benefit of these is that their smooth surfaces and even grains make for effective and accurate cutting, and laser plywood is cheaper than regular woods.
However, using plywood for laser cutting gives off dangerous fumes when laser cut, so you need a proper exhaust system in place.
If you’re a novice or a hobbyist you could greatly benefit from our guide to laser cutting plywood to get the most out of this material.
Particleboard
- Best for: all sorts of laser projects

Particleboard is a cheap engineered wood made up of wood chips with synthetic glue. As it contains glue, it’s best cut quickly with lower power settings to avoid over-melting the glue.
Particleboard is easily available and very versatile, so it’s a good option for all sorts of laser projects – just make sure your workplace is properly ventilated.
Woods You Should NOT Laser Cut?
Whereas there are virtually any types of wood that can be cut with a CNC router, you should avoid laser cutting the following:
- Oily hardwoods: Teak, bubinga, and santos mahogany, are particularly oily, making it difficult to get clean cuts.
- Resinous softwoods: For example ponderosa pine, these are prone to edge burning.
- Fiberboard & MDF: MDF is too dense to get good results, and the glue used can cause issues. It gives off formaldehyde gas when burnt, which is potentially hazardous.
- Exotic hardwoods: Tigerwood, Brazilian cherry, kempas, Australian cypress, and Sapele mahogany are extremely dense. This makes it difficult to get clean results with a laser.
- Pressure-treated woods: These contain fire retardants which can emit dangerous fumes when laser cut.
How To Pick The Right Wood For Your Next Laser Cutting Project
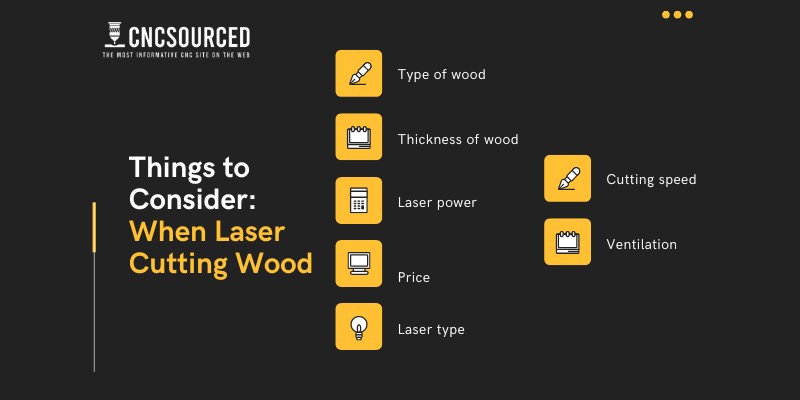
- Type of wood: Softwoods and hardwoods suit different products, and different woods also have different oil and resin content, which affects how easily they are to cut, and the quality of results. Engineered woods are easy to cut, but not all are suited to laser engraving.
- Thickness of wood: Some woods like oak and ash are much denser, affecting how deep you can cut with your laser.
- Laser power: More powerful lasers cut faster and deeper, for example, a 50W laser will cut deeper in a single pass than a 30W laser.
- Color and contrast: Different lasers produce different colorings on different woods.
- Price: Balsa and pine are cheap, whereas woods like mahogany are expensive.
- Laser type: CO2 lasers are generally preferred over diode lasers for woodworking as they have a 10,600nm wavelength that’s easily absorbed by wood and are more powerful, making them effective at cutting as well as engraving and etching. Fiber lasers are not effective for laser cutting wood.
Tips For Laser Cutting Wood
- Choose the right wood: For example, an archery bow requires a more elastic wood than a chair would, while projects like model airplanes require lightweight woods.
- Use proper ventilation: All woods produce fumes when laser engraved. So, it’s always important to have proper ventilation in place, by either using an extractor, or working outside.
- Ensure the wood is secure: Use a clamp or other means to avoid it jogging during the engraving or cutting process.
- Test your settings: Test your settings on a waste piece of wood before moving onto your project
- Finish the wood: You can brush away any debris, sand down if required, and then finish your wood. This helps the wood product last longer, and adds a nice sheen that makes it more attractive.